MagSafe 1 vs 2 vs 3
7 10 月, 2025USB 2 vs USB 3 — Full Comparison: Speed, Compatibility & Buying Guide(2025)
If you’ve ever wondered why one USB drive takes minutes to copy files while another finishes in seconds, the answer is simple — USB 2 vs USB 3. In this guide, we’ll break down every difference that matters — speed, power, compatibility, and which one you should buy today.
1. Quick Comparison: USB 2.0 vs USB 3.0
| Feature | USB 2.0 | USB 3.0 / 3.1 Gen 1 / 3.2 Gen 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Year Introduced | 2000 | 2008 |
| Theoretical Speed | 480 Mbps (60 MB/s) | 5 Gbps (625 MB/s) |
| Typical Real-World Speed | 30–40 MB/s | 350–500 MB/s |
| Power Output | 500 mA (2.5 W) | 900 mA (4.5 W) |
| Pins | 4 | 9 |
| Connector Color | Black / White | Blue |
| Backward Compatible |  Yes Yes |
 Yes Yes |
Bottom line: USB 3 is roughly 10 times faster and offers almost double the power.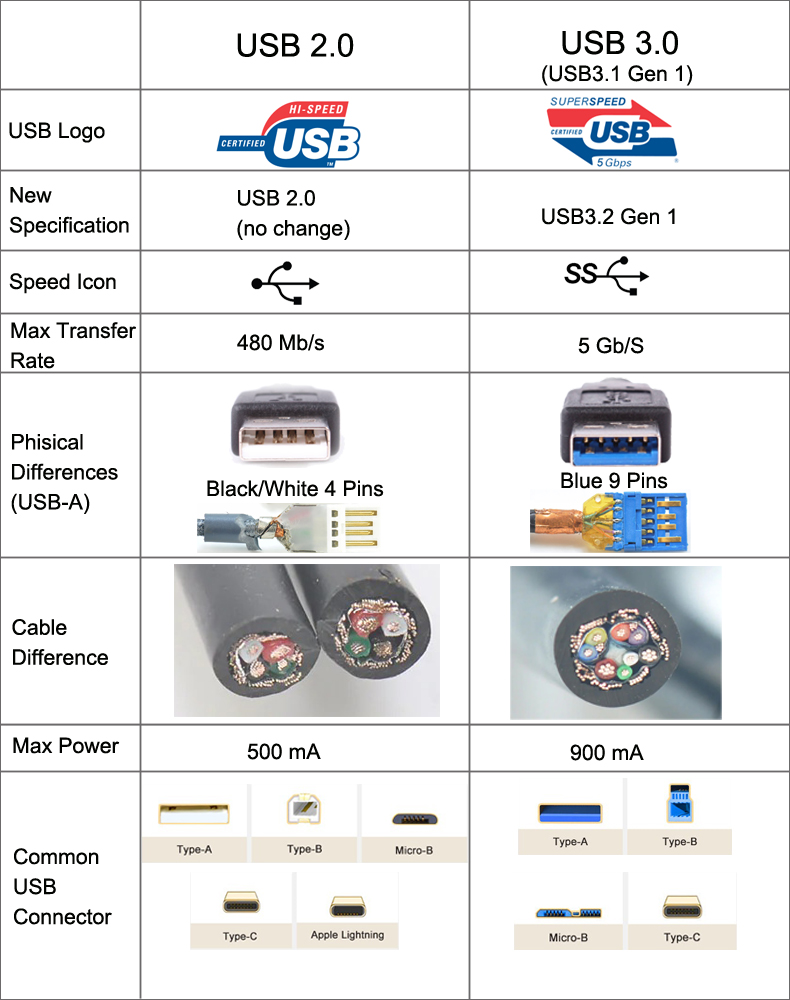
2. Evolution & Naming Confusion
The USB standard has evolved — and been renamed — several times:
- USB 3.0 (2008) → later renamed USB 3.1 Gen 1, then USB 3.2 Gen 1 (all = 5 Gbps)
- USB 3.1 Gen 2 = USB 3.2 Gen 2 (10 Gbps)
- USB 3.2 Gen 2×2 = 20 Gbps (dual-lane, USB-C only)
This naming confusion often misleads buyers. The key takeaway: If you see “5 Gbps,” it’s USB 3-speed no matter what it’s called.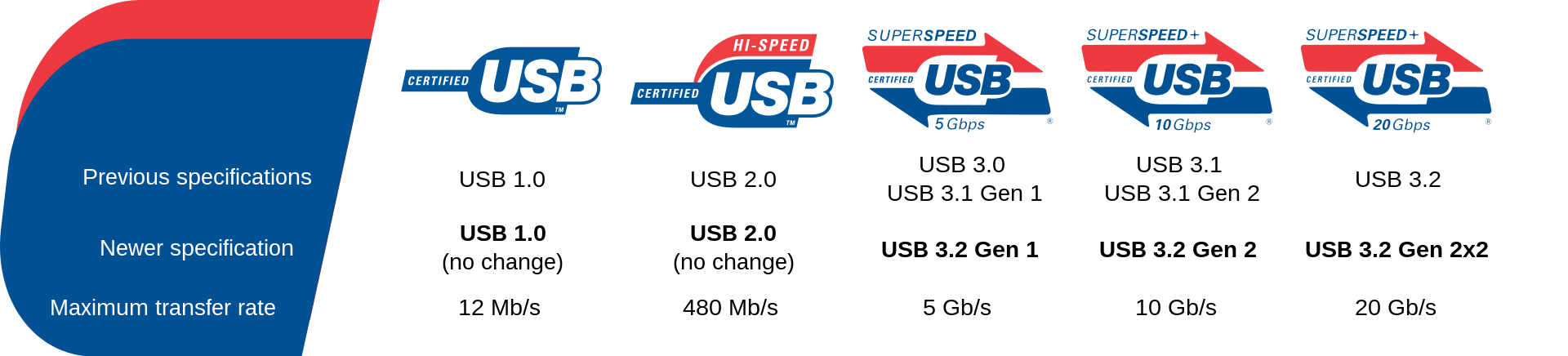

3. Technical Architecture Differences
Full-Duplex Transmission
USB 2.0 can only send or receive data at a time (half-duplex). USB 3.0 introduces full-duplex — simultaneous send + receive.
Wiring Structure
USB 3 adds four extra wires, totaling nine, allowing separate data lanes for each direction.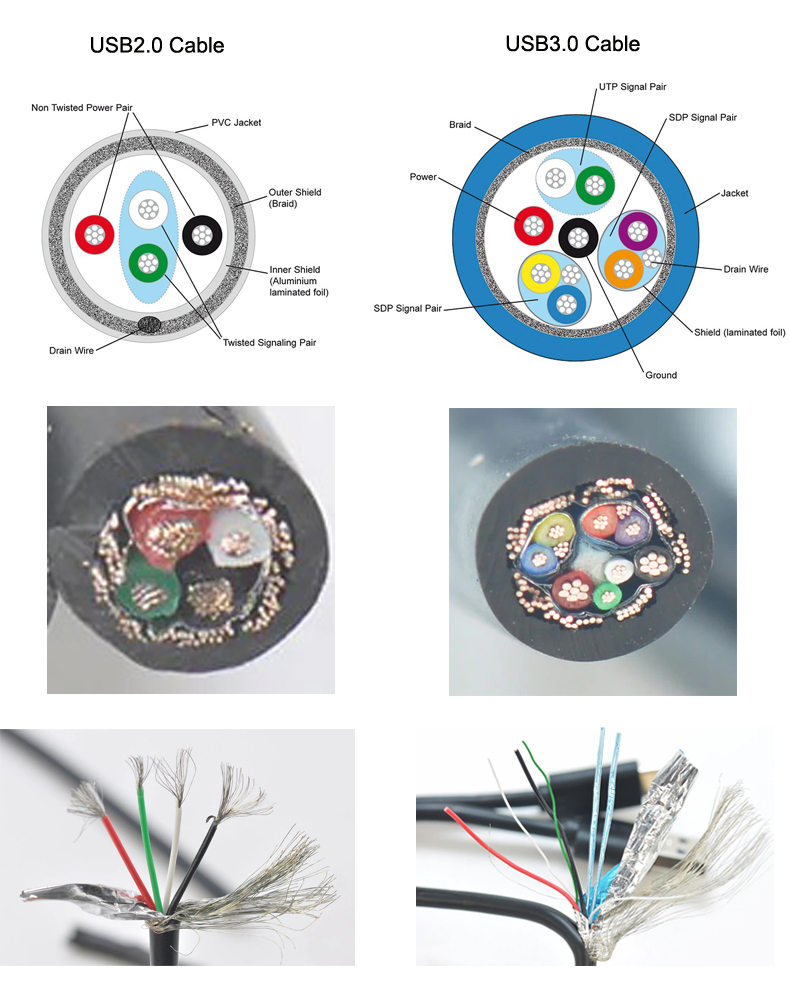
Encoding Efficiency
USB 3.0 uses 8b/10b encoding; later versions (USB 3.1 / 3.2) improve this with 128b/132b, reducing overhead and improving efficiency by ~20 %.
4. How to Identify USB 2 vs USB 3 Ports
You can spot the difference in seconds:
- Color:
- USB 2.0 ports are usually black or white.
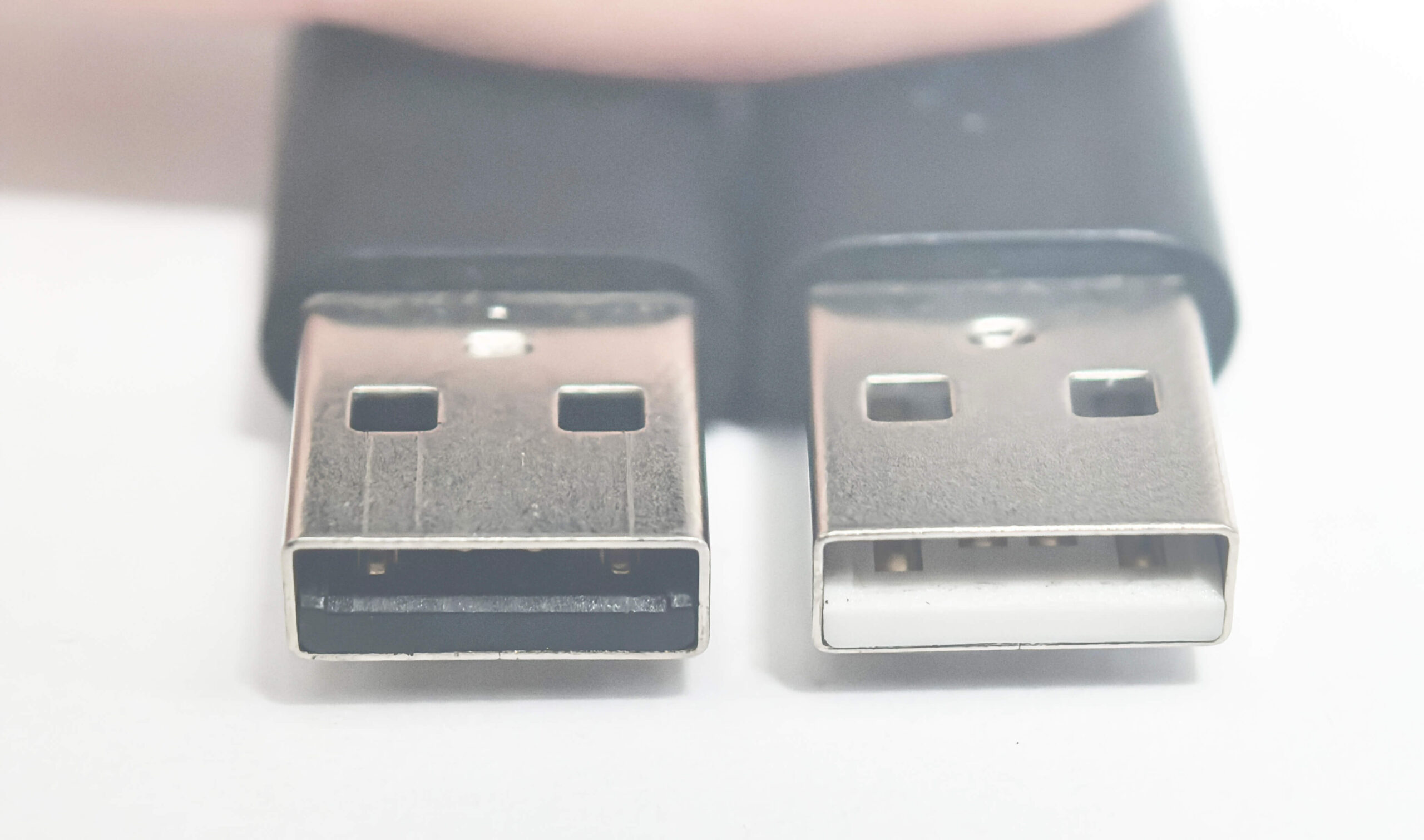

- USB 3.0 ports are blue.
- USB 2.0 ports are usually black or white.
- Labeling:
- USB 3.0 ports are often marked with “SS” (for SuperSpeed).

- USB 3.0 ports are often marked with “SS” (for SuperSpeed).
- Device Manager (Windows):
- Go to Device Manager → Universal Serial Bus Controllers and look for entries containing “USB 3.0” or “xHCI”.
That’s it — no guessing needed.
5. Real-World Performance & Power
Speed in Practice
- USB 2.0 tops out around 35 MB/s
- USB 3.0 reaches 350–500 MB/s (depending on device and cable)
Example: Copying a 10 GB video file takes:
- USB 2.0 → ~5 minutes
- USB 3.0 → ~30 seconds
Power Delivery
USB 3.0 provides up to 900 mA, almost double USB 2.0’s 500 mA. That means faster charging and support for more demanding peripherals like external SSDs and webcams.
6. Compatibility & Everyday Use
Can I plug a USB 2.0 into a 3.0 port?
Yes — they work together. The connection simply runs at USB 2 speed.
Can USB 3 fit in USB 2?
Yes. The connectors are physically compatible.
What happens if you plug a USB 2.0 into a USB 3.1 port?
It functions normally but transfers at USB 2.0 speed.
Can I plug a USB 2.0 into a 3.0 port on a motherboard?
Yes, motherboard ports are backward compatible with USB 2 devices.
7. Advantages of USB 3 Over USB 2
Is there a big difference between USB 2 and 3?
Absolutely — speed is up to 10× faster and power output almost double.
What is the advantage of a USB 3 port over a USB 2 port?
- Faster data transfer (5 Gbps vs 480 Mbps)
- Higher power (900 mA vs 500 mA)
- Full-duplex data flow
- Better efficiency and future-proof design
Is USB 3.0 necessary?
If you transfer large files, use external drives, or want faster charging — yes.
Is USB 2.0 still relevant today?
Yes — for keyboards, mice, and simple devices that don’t need speed.
8. USB-C vs USB 3 — What’s the Difference?
Is USB-C the same as USB 3?
No. USB-C refers to the shape of the connector, not the speed. You can have a USB-C port that runs at USB 2.0 speeds. Always check the specs for “SuperSpeed,” “5 Gbps,” or “10 Gbps.”
9. Buying Guide — Which Should You Choose?
| Use Case | Recommended Standard |
|---|---|
| Mouse / Keyboard | USB 2.0 |
| Printer / Scanner | USB 2.0 |
| Flash Drive / External HDD | USB 3.x |
| External SSD / 4K Video | USB 3.2 Gen 2 or Gen 2×2 |
| Fast Charging Devices | USB 3 or USB-C with PD support |
Tip: Always check both the port and cable support USB 3. If either side is USB 2, the speed drops to USB 2 levels.
10. Pro Tips for Manufacturers & Engineers
- Clearly label “USB 3.0 (5 Gbps)” on packaging.
- Include “SuperSpeed” logo or “SS” marking on cable plugs.
- Use 9-wire construction for certified USB 3 data cables.
- Test signal integrity and power delivery per USB-IF standards.
11. FAQ Summary
Are USB 2.0 and 3.0 ports the same size?
Yes, same dimensions; USB 3 has extra internal contacts.
Does cable length affect USB 3 speed?
Yes, longer cables (> 2 m) can cause speed loss and signal noise.
Can USB 3 cables power external drives directly?
Yes, many portable SSDs rely on USB 3 for power + data.
12. Conclusion — The Definitive USB 2 vs USB 3 Summary
Speed, power, and wiring make the difference.
- Speed: 480 Mbps vs 5 Gbps
- Power: 500 mA vs 900 mA
- Pins: 4 vs 9
Both standards are backward compatible, but for modern use, USB 3.x is the clear winner. It delivers faster data, better charging, and future-ready connectivity.
13. Overview
USB 3.0 is a major upgrade over USB 2.0. It’s up to 10× faster (5 Gbps vs 480 Mbps), delivers more power for charging (900 mA vs 500 mA), and uses more data lanes for higher performance. USB 3.0 ports are usually blue or marked “SS,” while USB 2.0 ports are often black or white. Both standards are fully backward compatible, but devices always run at the speed of the slower port or cable.
ON THIS PAGE
- 1. Quick Comparison: USB 2.0 vs USB 3.0
- 2. Evolution & Naming Confusion
- 3. Technical Architecture Differences
- 4. How to Identify USB 2 vs USB 3 Ports
- 5. Real-World Performance & Power
- 6. Compatibility & Everyday Use
- 7. Advantages of USB 3 Over USB 2
- 8. USB-C vs USB 3 — What’s the Difference?
- 9. Buying Guide — Which Should You Choose?
- 10. Pro Tips for Manufacturers & Engineers
- 11. FAQ Summary
- 12. Conclusion — The Definitive USB 2 vs USB 3 Summary
- 13. Overview



